As seen in
the previous post, a Computer Vision is a weird combination of Biology + Math + Computer science.
Global optimisation of images for further analysis using Bayesian Markov random field Models
After image processing is – “Feature detection and image segmentation” which I will cover in part 2 of computer vision post.
A glimpse of Feature detection and image segmentation
Human Eye is
an input layer from where the human brain receives the image data.
Processing
of image using different colour models happens in the human eye (using colour
models like RGB , CMYK , HSL , HSV ) human eye has a connection with the brain and desired output
is generated accordingly by Human Eye + Brain
Research
topics in the area of Computer Vision in the last 50 years.
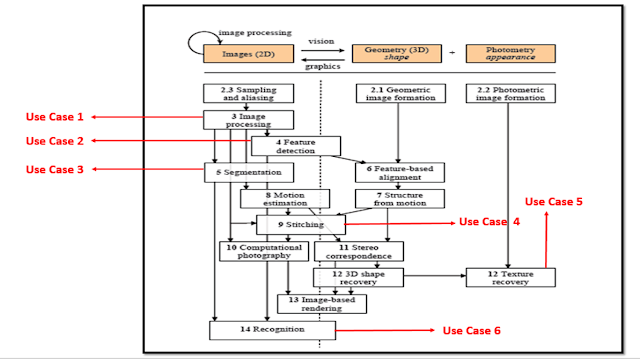
There are a
series of steps involved in the implementation of any Computer Vision
algorithm.
As seen
below each step can be a “Business Use
Case” for business men.
As seen
above in the 14th step of computer vision is – “RECOGNITION"
IMAGE
RECOGNITION is the latest discovery in Computer Vision which includes the following:
Object detection
Face recognition
Instance recognition
Category recognition
Context and scene understanding
Recognition databases and test sets
I will
cover the first 2 steps in today’s post (Image formation and Image processing)
This will be my PART 1 OF COMPUTER VISION post.
Image Formation:
Types of
Image data
Multi-spectral Image
Geospatial data
Clinical trial data – X Rays and Scan
Satellite imagery data
Digital data
Etc. and many more
Like human eye in computer vision - first a vocabulary has to be established to describe the
geometry of the image.
There are 2 Models for Image formation
Geometric Formation:
Geometric primitives
form the basic building blocks used to describe three-dimensional shapes.
2D Points are denoted by
Pixel value of the image.
Pixel values
are created for the images that is stored in the database and with the help of
pixel values - Points, lines, and planes
are introduced into the current image database.
With the
help of lines, equations are created as seen below.
Image Transformation:
After having defined our
basic primitives, image now has to be transformed.
The simplest
transformations occur in the 2D plane and are illustrated in below figure.
As seen below Image Transformation has following steps.
Translation: Translate
the data into a matrix
Rotation: Using
Euclidean distance
Transformation of the Image:
Affine Transformation and Projective / Perspective
Transformation
Same steps are also followed by the 3D Images for image transformation
except that different rotation techniques are used by 2D and 3D Images.
Difference between 2D
and 3D Image transformation can be studied more in the below link.
Below figure shows the 3D Image transformation models
The most commonly used
transformation in computer graphics is Perspective
Transformation
Photometric image formation:
Image cannot
exists without light
A particular
image is produced given a set of lighting
conditions, colour, and shadow and camera optics
In the
photo-metric image formation model - features like colour, shadow and light are
created for the current image database
Pixel values are influenced by the following features which are introduced into the current data model
Colour
Shadow
Light
Surface area of the object
Camera Optics
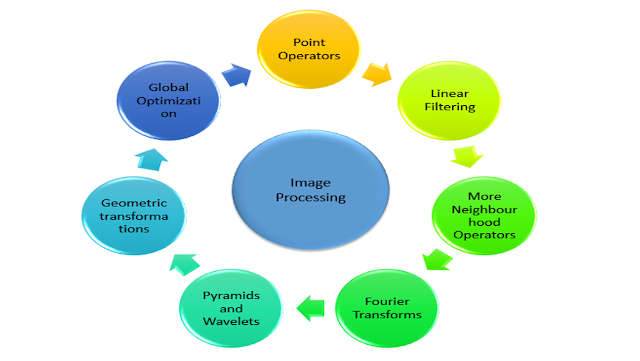
Image Processing:
We have seen
how images are formed through the interaction of 3D scene elements,Lighting,
and camera optics and sensors.
Image processing is like data cleaning
stage.
In this
stage the image is pre-processed and converted into database (analytical file)
which can be used for further analysis.
Examples of
pre-processing operations include
1. Exposure
correction
2. Colour
balancing
3. Reduction
of image noise
4. Increase
sharpness of the image
5.
Straightening the image by rotating it
I will not cover all the pre-processing methods ,and discuss only the main points
Point processing: Manipulating pixels independent of its
neighbours
Fourier Transform tool: The Fourier
Transform is an important image processing tool which is used to decompose an
image into its sine and cosine components
This is one of the most important Image processing technique
Global optimisation of images for further analysis using Bayesian Markov random field Models
After image processing is – “Feature detection and image segmentation” which I will cover in part 2 of computer vision post.
A glimpse of Feature detection and image segmentation












Comments
Post a Comment